Service Objectives
The following list represents the Key Service Objectives (KSO) for the Appleton Greene Launching Internationally service

Product Viability
In accessing product viability for international markets, it is important to also take into consideration some advantages and disadvantages of international trade which may be different in each of the global markets that are being considered. Advantages: Enhance your domestic competitiveness, increase sales and profits, gain global market share, reduce dependence on existing markets, exploit international trade technology, extend sales potential of existing products, stabilize seasonal market fluctuations, enhance potential for expansion of your business, sell excess production capacity, maintain cost competitiveness in your domestic market and expansion brought about by international trade could accelerate the advantages of taking your company public. Disadvantages: You may need to wait for long-term gains, need to hire staff to launch international trading, modify your product or packaging, develop new promotional material, incur added administrative costs, dedicate personnel for traveling, wait longer for payments?, apply for additional financing deal with special licenses and regulations , need to set up specialized and cost effective conferencing and communications tools. Other Considerations: During this phase a detailed review of the product or services will take place. Interviews with senior management, product marketing, product / technical support and engineering, if required will take place and a template will be defined that will govern the considerations and priorities of launching in North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East and Africa. Estimated market opportunity size will be a key part of this objective. Other considerations for each of these markets will include competition, target pricing, product modification requirements (if needed), human interface requirements, technical support, government regulations, homologation requirements, documentation and language considerations and Intellectual Property Rights protection.

Pre-launch Considerations
Mr. Nelson will be actively involved as a coach in all pre-launch and launch activities. Before discussing a successful launch, it is very important to consider some items that are sometimes are overlooked. These include the company not being able to support fast growth, the product falls short of claims and gets negative press or the product is “disruptive” but there is not a market for it. Therefore, the company needs a plan to ramp up quickly if needed, delaying the product launch until the product is ready and spending time to analyze the market and determining who will be buying the product and the needed price to be competitive. Other pre-launch considerations: Start early and not expect that t you will have immediate press coverage. Therefore, begin the preparation of the launch plans well in advance of the actual launch. Part of the launch plans should make the product available to key influencers as early as possible. These people should be targeted as potential resources to talk to the analysts about the product before the actual launch. These plans should also include the briefing of industry analysts early and writing compelling briefing requests. Remember, they will prioritize their time and therefore it is the client’s responsibility to insure that well stated white papers or other written documents are presented to convince them that their time is well invested if they provide the media coverage that is desired. In concert with these efforts seed the social space with carefully planned disclosures of “official information” by unnamed sources. Never plan for a major press release unless you have a truly “disruptive technology” that is actually available or you have a large product launch budget that includes not only paid for press coverage and a high profile launch events. Further, after the initial press releases, continue to provide additional new press announcements. These can include successful use cases, customer stories that preferably include their return on their investment by using the product. Channel partners are a valuable asset. Involve them early as they have a financial stake in the successful launch of the product. Having multiple sources talking about the initial product release increases the chance of additional press coverage. Subsequent, follow this “chat” and reach out to these sources to make them an ongoing ally. Another important tool, if used correctly, can seed the market quickly if the client provides free trials, product videos and / or other sales collateral early in the launch.

Launch Considerations
Marketing is at the core of an international product launch. A successful product launch would mean higher sales and production, whereas a launch that fails to market the new product effectively will cause a significant loss to the company. Companies face a number of problems and challenges in the process of launching their product. These obstacles do not stop at only national companies but are more evident and cause for concern in global launching. The most common and significant challenge in an international product launch would be the existence of varied cultures and the development of multi-cultural nations today. To increase cost effective value, durability and lifetime of products, companies speed up commercialization and face the challenging everyday economic changing trends. One of the biggest challenges in a global product launch is ensuring the delivery of accurate and current products and marketing materials to the correct distribution channels and sales groups cost effectively and securely. Some of the other challenges faced include supporting public relations across multiple markets, ensuring of consistent testing and qualifications, addressing the unique costs which associated with each individual country launch, ensuring that international requirements of products for marketing, QA, sales and engineering are met, planning press tours in multiple languages with the country specific presentations along with training sessions and seminars. When establishing growth targets, taking into consideration of the customer demographics or increased or decreased competition is crucial. A successful international product launch includes well-planned pre-launch and launch plans. Also critical is the alignment of all HQ departments. In an international product launch, throughout the entire process from designing the product, building it and managing the development of support and services is vital, especially for complex products . Other than being the first product in the market, innovative ideas and services of products is also a strong plus contributor to a successful launch. Adding to the challenge for a successful product launch are the product life cycles which are continuing to decrease while at the same time there is a rise in introduction to new products along with product complexity.

Channels to Market
No company can succeed; much less survive, without effective sales strategies. Two basic strategies are the direct sales channels and indirect sales channels. Understanding what these strategies mean and how they can best be implemented can are essential to long-term success. The most common definition of sales strategy deals with your approach to the customer. Direct sales requires a direct sales organization that sells the product or service directly to the end user customer. You can phone the customer, see her face to face or even use email. The communication link between the company and the prospective customer is direct. Direct or “business to consumer or business to enterprises” is one strategy. When engaging in indirect sales, a company uses some type of go-between and does not directly contact the customer, except for support when requested. The go-between could be a re-seller. There are several different re-seller profiles to be considered, depending on the market, product and end user. These channels include distributors, value add distributors, value add re-sellers, OEMs, and manufacturers’ representatives which are either commissioned or mark up the product prices to make their profit. Indirect is also known as B2B or business to business. Benefits of Both Sales Channel Strategies: One major benefit to a direct sales strategy is that you have a high level of influence on your customer and know exactly how your customer feels about your product or service because of the direct communication. A benefit to the indirect sales strategy is that the company can expand its geographic reach without having to hire a large sales organization. Another benefit to an indirect strategy is that oftentimes the costs associated with sales are directly in proportion to how successful the re seller is. While large markets, such as the US, have an enormous number of re seller’s, the real challenge is not finding re-sellers but to identify and recruit the ones that will proactively sell and market your product. Often companies have false starts in new markets because they just focus on signing up a large number of re-sellers that are purely opportunistic. Some key elements necessary to drive success include partner programs that defines the roles and responsibilities of all parties, compelling business terms that reward revenue growth by offering a tiered discount structure, a meaningful competitive differentiation, an ideal customer profiles and business scenarios, sales and technical training and a demand generating marketing programs. If selling via indirect channels, in the initial stages of penetrating a new market, the focus should be on making re sellers self-sufficient as quickly as possible through training and coaching so that you can realize the benefits of leveraging their organizations. Focus should also be on sales initiatives as opposed to marketing, being deliberate in targeting customers that can bring credibility and prestige to your customer list. Winning local reference accounts which can be leverage for future sales is critical to ongoing growth.

Gantt Chart
As outlined , a successful product launch is critical. The timing for a product launch must start many months before the actual launch. While consulting with senior management, product marketing, sales management, product support, technical support and product development to define a Gantt chart that defines the schedule and timing for, market / product viability studies, estimating market size, competitive analysis and researching government regulations. The market / product viability studies will determine if the products are viable for the targeted market. Government regulations, cultural restrictions, excessive costs to homologate, availability of the right professional sales and support personnel and import duties and tariffs , to name a few, may determine that the product is not viable. Estimating market size is critical. Depending on where a product is in its’ life cycle and other variables may determine that the size of the market may not justify the expenses to launch the product. Competitive analysis is critical as understanding where the competitors are in the market relating to their market penetration, product pricing, customization for particular market and product features and benefits to name a few . Researching government regulations is essential to determine if meeting government regulations can be met at a cost to support the market strategy. Sometimes it may not be feasible without spending a lot of money to meet the regulations. This includes the defining any homologation requirements and related costs. Critical to the Gantt chart is the allocation of timing for all pre-launch and launch activities. These are defined in the service objectives. This includes the recruiting of either the direct or indirect sales channels, developing the marketing collateral, press releases and content.
Telecommunications
Telecommunications is a universal term that is used for a vast range of information-transmitting technologies such as mobile phones, land lines, VoIP and broadcast networks and most networks casting are administered worldwide by an agency of the United Nations called the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). Most countries have their own agencies for enforcing the various regulations in their respective countries. There are many technologies which can be used to put together a network. These technologies include wireless devices like telephones, cellular, microwave, fiber optics, satellite and the telegraph. These technologies use a mixture of wireless and wire-line. However, the trend is to replace wire-line / cables with wireless as the time to deploy is significantly less, especially for long distances. A major consideration is also security. Whether using wire-line or wireless technologies, networks are quite vulnerable to being “hacked”. This major concern has spawned a new industry name cyber security. This is the science of protecting networks.
With the exploding industry sector referred to as IoT, or Internet of Things, many networks have new vulnerabilities as “sensors” are now wireless and can be “hacked”. These sensors are controlling power plants, homes, office buildings, utility companies, government networks, aircraft, ships, oil fields and manufacturing companies, just to name a few. The launch of telecommunications equipment and software globally is an enormous business opportunity, however highly regulated. Companies that have new technologies that protect , augment or provide telecommunications infrastructure has to carefully weigh the regulations governing these solutions in each country that they are targeting.
Technology
Technology is radically reshaping everything that we daily encounter. At the heart of most technologies are microchips , or miniature computers which are pervasive in every industry sector. This includes any type of computers, automobiles, airplanes, the space shuttle, all transportation devices, utilities, appliances, communications, power plants, robotics and drones, just to name a few. The exponential rate at which technology is being discovered, just in the last 25 years, is mind boggling. Can you imagine what our lives would look like if HIV drugs, genome sequencers, robotics space station, electric cares, wireless internet connections, the space station, landing on Mars, digital cameras, lap-top computers, smart phones, cloud computing, drones, fuel injectors, smart appliances Nano technology, pilot-less cars, and airplanes just to name a few?
Technology will become even more pervasive as the Internet of Things will bring more and more technology into our homes, offices, utilities, airplanes, cars, security systems, environmental monitoring and just about anything that is relying on sensor data. Technology has had a significant impact on the plummeting costs of energy. This has changed the way the world does business by reducing the costs of business to business transactions. These reduced transaction costs, driven by changes in government policies and improved communications infrastructure, have led to a wide array of business practices referred to as globalization. Companies that do not embrace technology cannot compete, therefore, the world is craving new technology. Hi-tech companies have an enormous opportunity by diversifying into international markets. However, this will require partnering with smart distributors, value added re-sellers and OEM’s that know their markets and how to introduce new technologies.
Utilities
The Challenges: Today, all utilities face a varied list of new threats and obstacles that force them to carefully examine their business model and operations core. There are many challenges that Utility companies are facing, economics being the first. For example, most developed countries utilities are growing more slowly. But they have enormous demands to increase loads in many areas while the infrastructure in many regions is aging. New regulations are forcing the capacity expansion with renewable energy and the replacement costs are high. While at the same time there is pressure to keep rate increases to a minimum, limiting investment capital. Many new technologies however, introduce uncertainty. An example is shale gas. While the technology has pushed down gas prices and has transformed North America’s previous dependencies on imported oil, we still do not understand what the impact can be on the environment.
The Opportunity: The principal public utilities are being maintained by local or state governments. All utilities are facing increased security requirements due to the dependencies that the mass population and governments have on electricity, water, gas and sewage. Therefore, technology and telecommunications companies have a large opportunity to automate the utilities’ Scada systems. This automation however, does not come without the need to be aware of the possible security impact that is widespread with the IoT “Internet of Things” proliferation going forward. IoT will be the wave of the future. Utility companies can install wireless sensors, security cameras, VoIP (voice over IP) and WiFi networks to communicate with the outside world, if and when needed. Scada networks will also need revamping to comply with IoT standards. Therefore the technology, telecommunications , Scada and security sectors have enormous opportunities in most international utility markets.
Bronze Service
 Monthly cost: USD $1,500.00
Monthly cost: USD $1,500.00
Time limit: 5 hours per month
Contract period: 12 months
Bronze service includes:
01. Email support
02. Telephone support
03. Questions & answers
04. Professional advice
05. Communication management

SERVICE DESCRIPTION
The Bronze Client Service (BCS) for Launching Internationally provides clients with an entry level option and enables client contacts to become personally acquainted with Mr. Nelson over a sustainable period of time. We suggest that clients allocate up to a maximum of 5 Key Employees for this service. Your Key Employees can then contact the consultant via email, whenever they feel that they need specific advice or support in relation to the consultant’s specialist subject. The consultant will also be proactive about opening and maintaining communications with your Key Employees. Your Key Employees can list and number any questions that they would like to ask and they will then receive specific answers to each and every query that they may have. Your Key Employees can then retain these communications on file for future reference. General support inquiries will usually receive replies within 48 hours, but please allow a period of up to 10 business days during busy periods. The Bronze Client Service (BCS) enables your Key Employees to get to know their designated Appleton Greene consultant and to benefit from the consultant’s specialist skills, knowledge and experience.
Silver Service
 Monthly cost: USD $3,000.00
Monthly cost: USD $3,000.00
Time limit: 10 hours per month
Contract period: 12 months
Bronze service plus
01. Research analysis
02. Management analysis
03. Performance analysis
04. Business process analysis
05. Training analysis

SERVICE DESCRIPTION
The Silver Client Service (SCS) for Launching Internationally provides more time for research and development. If you require Mr. Nelson to undertake research on your behalf, or on behalf of your Key Employees, then this would understandably require more time and the Silver Client Service (SCS) accommodates this. For example, you may want your consultant to undertake some research into your management, performance, business, or training processes, with a view towards providing an independent analysis and recommendations for improvement. If any research and development, or business analysis is required, then the Silver Client Service (SCS) is for you.
Gold Service
 Monthly cost: USD $4,500.00
Monthly cost: USD $4,500.00
Time limit: 15 hours per month
Contract period: 12 months
Bronze/Silver service plus
01. Management interviews
02. Evaluation and assessment
03. Performance improvement
04. Business process improvement
05. Management training

SERVICE DESCRIPTION
The Gold Client Service (GCS) for Launching Internationally is intended for more detailed evaluation and assessment, that may require your Key Employees to have monthly meetings or interviews with Mr. Nelson. These meetings and interviews can be conducted over the telephone, Skype, or by video conference if required. The consultant can also attend your business premises, an Appleton Greene office, or another mutually beneficial location, but please note that clients are responsible for the costs of any disbursements separately, including travel and accommodation. This service enables you to integrate the specific skills, knowledge and experience of your designated consultant into your Key Employee management team. The Gold Client Service (GCS) can also incorporate training workshops, business presentations and external meetings with customers, suppliers, associations, or any other business-related stakeholders.
Platinum Service
 Monthly cost: USD $6,000.00
Monthly cost: USD $6,000.00
Time limit: 20 hours per month
Contract period: 12 months
Bronze/Silver/Gold service plus
01. Project planning
02. Project development
03. Project implementation
04. Project management
05. Project review

SERVICE DESCRIPTION
The Platinum Client Service (PCS) for Launching Internationally is our flagship service and will be required if you need Mr. Nelson to facilitate the planning, development, implementation, management, or review of a particular project relating to his specialist subject, which would obviously require more time and dedication. This service enables you to reserve up to 12.5% of the consultant’s working month and provides a more hands-on service as and when required. If you need more time than this, then this can always be arranged, subject of course to the consultant’s ongoing availability. The benefit of having an external consultant involved in projects is they provide an independent perspective and are not influenced by internal politics, day-to-day responsibilities, or personal career interest. They provide objectivity, specific knowledge, skills and experience and will be entirely focused upon the tasks at hand. The Platinum Client Service (PCS) will provide your organization with a valuable resource as and when you need it.
Service Benefits
Globalization
- Business development
- Strategy formulization
- Global branding
- Vision
- Cost effectiveness
- Global partnering
- Wider market
- Leverage capacity
- Diversification
- Company valuation
Management
- Improved profits
- Increase revenues
- Strategic direction
- Minimize risk
- Strategy development
- Competitive advantage
- Shared vision
- Corporate effectiveness
- Resource alignment
- Compliance accuracy
Human Resources
- Reduced uncertainty
- Team effectiveness
- Decreased turnover
- Competitive advantage
- Lower costs
- Workforce loyalty
- Organizational efficiency
- Decrease risk
- Diversity
- Recruitment efficiency
Clients

This service’s current clients or employers include:
Polymer Aging Concepts
R & D company focused on deploying an IPR protected technology that will detect the aging of polymers. Polymer Aging Concepts has developed a simple, low-cost thermal age sensor called AgeAlert that can be used to project the remaining useful thermal life of virtually any product that degrades due to temperature and humidity. This wired or wireless sensor, bonded to the monitored product or product packaging, constantly integrates the aging effect of temperature for virtually any product for which thermal aging data is available. The heart of AgeAlert tag technology is a patented conductive composite sensor that measures the changes in resistance with its integrated thermal history. AgeAlert sensors eliminate the need for thermal data logging to provide the effect of a complex thermal environment. Products/Services: Polymer Aging Concepts, Inc. has demonstrated degradation-sensing technology for electrical equipment such as motors and generators, transformers, and wire/cable insulation. First product introduction for motor/generator winding applications is scheduled for early 2010. The company will leverage AgeAlert technology for sensors in related materials such as wire and cable products, industrial rubber products, automotive tires, and transportation infrastructure such as asphalt pavement. Additional research will open additional markets to patented AgeAlert technology including food products, pharmaceutical products, building materials, composite structures, solid propellants and ordnance. Polymer Aging Concepts is aggressively pursuing Small Business Investment for Research funding and strategic partnerships to develop these additional product areas. Technologies/Special Know-how: Polymer Aging Concepts, Inc. owns the intellectual property for AgeAlert technology through four pending US patent applications and two international patent applications. Its close association with Georgia Tech provides an established research and development infrastructure capable of rapid product engineering for its customers.

OpenWave
OpenWave is a leading innovator of software applications and infrastructure solutions, OpenWave Systems (NASDAQ: OPWV) enables revenue-generating personalized services in the mobile and broadband space. OpenWave Mobility empowers mobile operators to manage and monetize encrypted and unencrypted traffic. We have a rich legacy. At the turn of this century OpenWave Mobility (then Phone.com) invented the mobile internet by creating foundational technology including HDML and as a founder member of the WAP Forum. Today we offer the industry’s most scalable NFV platform and using this our solutions alleviate RAN congestion, create new revenue opportunities and unify subscriber data. Our company provides solutions to mobile operators for Traffic Management and Subscriber Data Management. OpenWave Mobility has deployed all-IP traffic solutions with over 40 of the world’s largest service providers, and today provides services utilized by more than 1.5 billion subscribers. The company has built a robust portfolio of Intellectual Property, which is growing month by month and today has a global presence headquartered in Silicon Valley California. OpenWave Mobility is owned by Marlin Equity Partners, a leading investment firm with over two billion dollars of capital under management.

Digital Communication Associates
Digital Communication Associates, short DCA, is a company in the telecommunications industry, which was located in Alpharetta, Georgia, United States.Digital Communications Associates was founded by John Alderman, who led the company until 1981, when he was replaced by Bertil Nordin. In February 1983, DCA went public, raising 24 million USD Later, Garry Betty (1958-2007) was CEO of DCA, until he left for Earthlink in November 1996. Together with Intel, DCA had designed the DCA/Intel Communicating Applications Specification (CAS). It defines a standard, high-level programming interface for data communications applications. The DCX format is the standard file format for storing FAX images in CAS. DCA was in the market of producing T-1 multiplexers. In 1994, DCA of Alpharetta, Georgia, was acquired in 1994 by Attachmate Corporation of Bellevue, Washington. In 1981, under the leadership of Bertil Nordin, DCA acquired Technical Analysis Corporation (TCA), the makers of the Irma Board which enabled PCs to function as 3270 terminals to an IBM mainframe. In September 1986, DCA bought Cohesive Networks. In 1986, DCA acquired Microstuf, makers of the Crosstalk Communications package together with their flagship product, the terminal emulation program Crosstalk. In 1991, DCA acquired Cincinnati-based InterComputer Communications Corporation (ICC), makers of the INFOConnect line of terminal emulation and file-transfer products (focused on the Unisys ecosystem), OpenMind (collaboration) and RLN (remote lan node).

Digital Transmission Systems
Digital Transmission Systems, Inc. manufactured a range of products for the telecommunications industry. Its proprietary products facilitate network access, bandwidth management, network control, and delivery of digital telecommunications services. The company’s products include Microflex, Flext1 and Flexe1 product family, Flext1/E1 System Architecture, IP Processor products, and Interflex. Its primary customers are long-distance carriers, domestic and international wireless service providers, and domestic and international re sellers/integrators. In January, the company approved an Employee Stock Ownership Program (ESOP) that would purchase all DTS equity instruments held by Wi-LAN. Manufacturer of components designed to build, access and monitor high-speed telecommunications networks worldwide and wireless spread spectrum radios. The company’s components and products include the FlexT1/FlexE1 integrated network access product lines and microFlex cross connect systems enabling domestic and international wireless service providers, telephone service providers and private wireless network users to access equipment performance at remote cell sites with an internet or intranet interface.

FreeWave Technologies
A global leader in industrial wireless and military unmanned systems, FreeWave Technologies provide critical communications solutions to government, public utilities, military, and commercial clients. FreeWave is uniquely positioned to understand and address many of the wireless networking challenges that have surfaced due to the widespread proliferation of “The Internet of Things” They have delivered world class IoT platforms to thousands of industrial and unmanned systems customers. With that experience, they are now focused on the deployment of intelligent applications at the edge of industrial networks and unmanned systems. With over 20 years of RF innovation under its belt, FreeWave is the undisputed leader in military unmanned systems and industrial wireless. Millions of our best-in-class, outdoor, ruggedized radios have seen action in some of the most harsh and dangerous places in the world. Our new Industrial IoT (IIoT) programmable radio platform makes Fog Computing, M2M and the Intelligent IIoT a reality. If it’s mission-critical intelligent wireless, it’s FreeWave.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

Atlanta GA
Atlanta’s international profile continues to rise. This year, Atlanta was ranked sixth in the world by A.T. Kearney’s Global Cities Outlook for its opportunity to be one of the most competitive, influential cities in the world. Additionally, the Brookings Institution named Atlanta as one of 19 “knowledge capitals” in the world, attributing to its’ talented workforce, research institutions, and role as a growing innovation center. Supporting this growth in international exports, the Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport is the world’s busiest and most efficient passenger airport for the 18th consecutive year. Atlanta hosts a large number of telecommunications / technology companies and several “technology incubators”. This positions Atlanta technology companies to be at the forefront of looking for international expansion. Atlanta has also become a favorite “film making city”, also fanning technology companies to support the growth in this industry. Atlanta is also an attractive U.S. destination for foreign direct investment. In the last twelve months, two large companies, Germany-based Bauerfeind, U.K.-based Sage Group PLC, and Brazil-based Merchant e-Solutions relocated their North American Headquarters. This has created more than $13M of foreign investments in Atlanta, creating more than 600 jobs. In effort to further Atlanta’s foreign investment strategy, Atlanta has the Metro Atlanta Foreign Direct Investment plan as part the second phase of the Brookings Institution’s Global Cities Initiative here in Atlanta. Through this strategic effort, Atlanta is better equipped to attract international investment. This will strengthen Atlanta’s economy and create stable, high-paying jobs for a talented workforce. Atlanta’s exports have also increased by $1.3 billion since the launch of the Atlanta Metro Export Plan (Atlanta MEP). There have been multiple missions to seven countries including Cuba, Japan, France, the United Kingdom, South Africa, and Singapore. Atlanta is well positioned to continue to elevate its international presence. For international companies wishing to launch in Atlanta, there is an excellent labor pool of professionals and possible investment funds available to set up in Atlanta. There is also an active hi-tech community and appetite for telecommunications, technology and utility technologies. Major Atlanta based international companies include Delta Air Lines, Coca Cola, Home Depot, United Parcel Service, Georgia Pacific, NCR, EarthLink, Oxford Industries and Race Trac Petroleum. In addition over 75% of the Fortune 1000 companies have a presence in the Atlanta area, and the region hosts offices of about 1,250 multinational corporations.

Beijing CN
Beijing, previously named Peking, is the capital of the People’s Republic of China and the second most populous city in China with more than 22 million people. The city, located in northern China, is governed as a municipality under the national government with 16 districts. Beijing is the second largest city in China, just after Shanghai with 24.1 million in 2017. Beijing is also home to the headquarters of most of China’s largest state owned companies. Beijing is rich with ancient culture and has seven UNESCO World Heritage sites. Beijing also has 91 universities which are constantly ranked the best in China. For western companies looking to have a presence in China, a labor pool of well qualified and educated English speaking professionals are readily available. Please note that today there are 52 of the fortune 500 companies have their HQ in Beijing, more than any other city in the world. Mr. Nelson represented multiple high tech companies over the past 30 years. During this time, a substantial part of his focus and revenues have come from China. When I first traveled to China in 1995 cars were extremely rare, mobile phones were non-existent and when I needed to make an international call, it was booked in advance with the hotel operator. Today, Beijing has traffic jams that consist of cars, bicycles, and people pulling rickshaws or other human pulled contraptions. While, walking down a street in Beijing all professionals and university students will be talking on cell-phones. It is also not possible to walk anywhere that you will not see massive new construction projects. Western technology companies wishing to do business in China that provide wireless telecommunications, SCADA , drones, network security and IoT technologies will find an eager market. However, I do not recommend a “direct sales organization” from the onset. Rather, partner with some of the hundreds of hi-tech re-sellers that are always looking for western technology. There are also many excellent, English speaking re-seller organizations looking for western technologies. Noteworthy, is that other large Chinese cities like Shanghai, Nanjing, and Guangzhou. Shenzhen, Hangzhou, Chengdu, Xi-an and Chongqing, to name a few, all have representation that is either HQ or local presence in Beijing. While looking at international companies based in Beijing, it is important to remember that most large Chinese companies are owned by the government. These companies include Air China, Lenovo, Datang Telecommunicatioins, Bank of China, China Petroleum Company, China Mobil, China Unicom and China Satellite Communications Company.

Paris FR
Paris is the capital of France and most populous city of France, with a population of 2.2 million. The “Paris region” has a 2016 population of 12.1 million, which represents 18% of France’s population. Paris is one of Europe’s major centers of finance, commerce, fashion, science, and the arts. The Paris region is France’s leading economic region and one of Europe’s foremost business hubs. The Paris region represents 31% of the French nation’s GDP and 4.6% of the European Union’s GDP, ahead of Greater London. The GDP of Paris is approximately 1/3 of France’s GDP of $2.5 Trillion $ in 2016. According to official estimates, in 2013-14 the Paris Region had the third highest GDP in the world and the largest regional GDP in the European Union. Paris is also acclaimed for its’ air-transport hub served by two international airports: Charles de Gaulle and Orly. The Paris region brings together a high density of technology companies including many startups and is and one of Europe’s highest concentrations in the science and technology sectors. For this reason France and the Paris region in general, is an ideal location for French companies to be looking at launching their technology outside of France and for non-French companies to be looking at how to penetrate the French market, especially in the Paris region. The Paris region is also known for its excellent education system and has a highly qualified workforce that provides 23% of the jobs in France. A few of the international companies based in Paris include, AXA, Total, BNP, Carrefour, Airbus, Astrium Industrials, Citroen, Michelin, Sagem, Thales Group and Thompson CSF.

London UK
“London is the most influential city in the world”, according to Forbes in 2014. London is also a major European economy. The Gross Output per person in London is more than double than the rest of the UK. Also noteworthy, according to many financial analysts, is that all cities in the UK except London were still worse off than they were before the financial crisis. However, overall the UK trade deficit narrows even in light of the UK exit (Brexit) from the European Union. London also contributes 22% of the UK GDP although London only represents 12.5% of the UK population. London is a financial power house. Canary Wharf, London’s Wall Street, is one of the biggest financial centers in Europe. More than one half of the top 100 listed companies (FTSE 100) also have their HQ in London. Further, 75% of the Fortune 500 also have offices in London. London also has 485 overseas banks, more than any other city in the world. London is also prime for technology, telecommunications and utility centric exports. A very large concentration of small, fast growing technology companies are also concentrated in London. Also noteworthy, is a large growing number of technology companies that are making their home in the “Silicon Roundabout” also located in London and is and these firms are poised to take advantage of Global emerging markets. A 45 minute rail ride will take you to Cambridge that is home for many hi-tech companies and is also a technology incubator. Cambridge also has several universities and has an excellent pool of well-trained technology professionals. A few of the London based international companies include HSBC, Royal Dutch Shell, BP, Barclays, GlaxoSmithKline, Aviva, UniLever, Vodafone, Anglo American, Tesco, Prudential, Astro Zinica, Rio Tinto, BT Group and UBS.

Amsterdam NL
Amsterdam is the financial and business capital of the Netherlands. Many foreign companies have chosen Amsterdam as their first international outpost. It has an excellent labor pool of professionals and is extremely hospitable to foreigners. Amstelveen, a municipality in the Netherlands and is a suburban part of the Amsterdam metropolitan area is an ideal place to locate their initial entry in Europe. 180 nationalities live in Amsterdam, making it the most international city in the world. Europe may be physically small when it comes to continents, but its compact size has done nothing to curtail its vast range of languages and different cultural practices. Therefore, having an effective entrance into the European market relies on your ability to localize – something which the diverse population of Amsterdam can easily accommodate. In addition, Amsterdam is one of the few European cities that is comfortable operating in a non-native language. The Dutch are far and beyond the best non-native English speakers in the world and they have a grasp of the language that is arguably better than the average foreigner. Only the UK and Ireland has a better English comprehension in Europe and outside of North America. Language is an essential ingredient for doing business (if English is your company’s language of operation) and perhaps one of the driving factors for companies choosing London, Dublin or Amsterdam for their European HQ. However, where the Netherlands beats London or Dublin is in the diversity of other languages spoken. As an example, 71 percent of IT-related professionals can also speak German (Germany is the United States’ largest European trading partner) and 29 percent speak French, which is essential for capturing the Benelux region. Add this to the 180 different nationalities in the city and you have some very useful skills that can be offered to businesses in the early stages of their first European / International venture. It is also to be noted that Schiphol airport offers an incredible number of connecting flights all over the world – with 70 direct daily flights to London, a dozen to New York, and even a handful for the 11+ hour slog to San Francisco. A few of the major international companies based in Amsterdam include American Express, Cisco, KLM, Logica, Mattel, Marriott International, Nike, Philips, Sony and Tommy Hilfinger.
Testimonials

Polymer Aging Concepts
“I have worked with Mr. Nelson for a number of years. His skill sets in management, consulting, marketing sales and investment are unparalleled. He takes command of opportunities and closes the deal. And he does it in a respectful person-to-person environment. Couldn’t recommend him more highly!”

FreeWave Technologies
“Mr. Nelson has a tireless work ethic and is willing to do what is necessary to be successful. He has an extensive international background. While at FreeWave, he built reseller partner coverage models in Asia Pacific, Latin America and the Middle East by leveraging some of his long term contacts and extensive international experience. He has demonstrated expertise and developed opportunities in “IoT” wireless communications for “Smart Utilities”, “Smart Cities” and Oil and Gas SCADA networks. Mr. Nelson has a passion for international sales/business development, respected by his peers, is a team-player and willing to work hard to build the business from the ground up.”

Pacific Advantage International
“As CEO of Pacific Advantage, I have worked with Mr. Nelson while he held international sales management positions with three different companies. He is a top professional in the international business area and knows the right partners, the right process to engage them and how to drive large sales opportunities. Pacific Advantage has worked on projects with Mr. Nelson that include IoT wireless solutions including Smart Cities, Smart Utilities, Enterprise / Government Security, SCADA Networks and Cyber Security. However, I can recommend Mr. Nelson to any technology company seeking to expand internationally and would be available to speak live should that be needed as well.”
Personal Profile
Mr Chicles is an approved Certified Learning Provider (CLP) at Appleton Greene who is a business leader and strategist with broad experience in the global multi-industrial, aerospace and defense sectors. He is a seasoned operational leader of global industrial businesses, leading transformational strategies in highly competitive markets.
As a senior, C-suite strategist for multiple major industrial corporations he has led multiple mergers, acquisitions, divestitures and restructurings, as well as corporate break-ups and spin-offs. He has a distinguished track record of successful transformations of complex organizations in dynamic and uncertain market conditions while engendering the trust and buy-in of employees, customers, vendors, owners, corporate leadership and boards of directors.
A highly engaged leader at the personal and team level he has demonstrated the ability to engender effective senior teams and boards. He’s also an active mentor, teacher and community leader.
Mr Chicles is an active board member with AES Seals, global leader in sustainable reliability engineering, and Micro Technologies Inc, an electronics and advanced manufacturing company. He is a principal partner with ProOrbis Enterprises®, a management science consultancy with premier clients such as the US Navy and PwC, as well as the principal of Xiphos Associates™, a management and M&A advisory. Recently, he served as Board Director and Chairman of Global Business Development with Hydro Inc. the largest independent pump and flow systems engineering services provider in the world.
He was President of ITT’s Industrial Process / Goulds Pumps business segment a global manufacturer of industrial pumps, valves, monitoring and control systems, and aftermarket services for numerous industries with $1.2 billion in revenue, 3,500 employees and 34 facilities in 17 countries. Preceding this role he served as Executive Vice President of ITT Corporation overseeing the creation of a newly conceived ITT Inc. following the break-up of the former ITT Corporation to establish its strategy and corporate functions such as HR, communications, IT and M&A, building the capabilities, policies and organizations for each.
He joined ITT Corporation’s executive committee as its strategy chief in 2006 and instituted disciplined strategic planning processes and developed robust acquisition pipelines to respond to rapidly changing markets. Created successful spin-offs of 2 new public corporations Exelis Inc. and Xylem Inc. ITT Corporation was named one of “America’s Most Respected Corporations” by Forbes for exemplary management and performance during his tenure there.
Before joining ITT, Mr Chicles served as Vice President of Corporate Business Development and head of mergers and acquisitions for American Standard / Trane Companies, where he initiated and closed numerous transactions and equity restructurings globally.
Additionally, he created and led the corporate real estate function which entailed more than 275 real estate transactions around the world.
He began his career at Owens Corning rising through the ranks in various operational roles to Vice President of Corporate Development.
Recently, he taught advanced enterprise strategy at Stevens Institute of Technology as an adjunct professor and still supports start-ups through the Stevens Venture Center. He continues to be active as the Founding Board Member with several successful start-up technology businesses and non-profit organizations. A community leader, Mr Chicles has held the role of President of the Greek Orthodox Cathedral in Tenafly, N.J., He also led trips abroad to Cambodia and Costa Rica to build sustainable clean-water solutions and affordable housing.
His formal education includes earning a Masters of Business Administration from The Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania, and a Bachelors in Finance from Miami University.
(CLP) Programs

Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.

Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary

Acquisitive Growth
In today’s context of changing markets, technologies and business models, and in conjunction with historic levels of available capital, acquisitive growth has emerged as an increasingly compelling approach to transformational growth. However, as has been empirically proven growth through acquisitions is fraught with pitfalls and inherently risky. Successfully acquisitive growth requires the confluence of many factors that go beyond the traditional phased steps of a typical process. In my experience success is a function of bringing together the elements of people, processes, and technologies into a set of capabilities that are custom-made for an organization’s particular strengths, circumstances and aspirations. Winning in today’s dynamic markets demands bold, unique and sustainable strategies. The following are the stages of such an approach that I have found to create high probability, profitable growth that stands the test of time.
Additionally, while the M&A industry has many advisors available, they tend not to be operating executives who have lived through all the elements I will lay out below. Many simplistic guidelines exist, however what its clear is that the difference between success and failure with acquisitive growth is not in rote adherence to some set of processes, rather it is found in the combination of process discipline and strong application of experiential, practical knowhow. The nature of this knowhow is to apply and allocate the elements below in a smart, efficient manner to achieve exemplary outcomes for the specific client’s unique situation and circumstances.
Strategy Development: Whether at the corporate level or in a specific business unit, clients would be taken through steps to clarify the markets and segments where they currently compete and where they want to go in the future, what differentiates them from competition, where capabilities need to be refined or built, and the various functional elements (e.g. systems, processes, structures, etc.) critical to sustain profitable growth. Approach would be a combination of review of current strategies/capabilities, interviews and facilitated discussions and structured workshops. Outcomes might be a strategy to bring a particular business into a new growth phase or to meet changing competitive environments, or at the enterprise level might entail “platform building” whereby new businesses, sectors or legs are build from the ground up through foundational initial acquisitions and subsequent organic and inorganic initiatives.
Market Focus: Where will we hunt for acquisition targets? If a company allows too-wide of a scope will find themselves suffering from expensive resource drains/distractions and/or dilute efforts. Therefore, following the alignment of enterprise/business strategies the process will seek to focus the market segments and the business criteria to qualify a company to be elevated to possible target.
Research Possible Targets: Simply put, take the descriptions and criteria from above and create lists of potential targets that might fit. Each such company is researched for available information, any currently available knowledge the client might have, etc. Output is a gross list of possible targets.
Target Approach: Utilizing a number of possible approaches, one that is appropriate for the client is determined. For example, some companies may have business development or sales teams who could participate in this stage, or on the other hand for reasons such as confidentiality, resource scarcity, etc this might need to be put into the hands of specific individuals (senior executives, dedicated M&A executives, 3rd party services, etc.). Each company is different, so this is an exercise of matching needs with capabilities. The objective is to screen the gross target list to elminate those who have “killer facts” such as big contingent liabilities, prohibitive complexity such as a company with a complex ownership structure, our any other aspects that renders a target not acceptable for the next step.
Cultivation: This is a very critical part of the overall process. The essence of this authentic, genuine and meaningful relationship-buidling which requires a combination of individuals with certain skill-sets to ‘sell’ the prospects on being acquired, patience and persistence. I have many approaches, processes and techniques that I have and continue to use to great effect in this regard. Output is a short list of interested targets who have moved to active discussions and in-person meetings.
Target Assessment: During the cultivation phase as it gets more advanced, a critical success factor for effective acquisitive growth is the ability to narrow the list with limited amounts of information. This is important because the next phase is quite intensive so any company can not practically thoroughly assess all such targets. In other words, how does a client gain the insights needed to do this? Some might consider this the ‘phase I due diligence’ whereby, prior to the engagement of expensive resources such as lawyers, accountants, etc., an overview of a target’s current status is determined. Through structured and open discussions, the client engages in discussions with the targets to learn as much as possible..
Preliminary Offer: Structuring of a term sheet or letter of intent based on finding to date. Depending on these findings, certain terms may be included to lay out a) value expectations; b) focus for due diligences and commitment to support it; and c) various legal terms typical for these agreements. This tend to be non-binding agreements meant to establish exclusivity of dealings for a period of time, high level terms that both parties agree to, and confidentiality. Given my background, I have the abilility to craft these documents with minimal legal cost.
Due Diligence: This is yet another element of acquisitions that can take several different forms. Depending on the situation and capabilities of both clients and targets, due diligence activites tend to have different scopes and approaches that match each particular circumstance. A simple example would be a private company target versus a public company. With the latter, sellers often limit potential acquirers to only publicly available information whereas private companies may have limited information at their disposal. Therefore, each approach must be designed for purpose, with the output being a customized plan for a particular target. This leads to both more efficient and cost effective processes as well as deeper insights to help with final decisions.
Deal Making: After the due diligence phase, and with a set of terms already agreed, the negotiations begin to finalized the terms of value, liabilities and the myriad legal and busses considerations that must be addressed and finalized. Whether as chief negotiator or as a trusted advisor to the same, I would bring my experience and talent to bear on this phase as well as some structured approaches/guidelines.
Integration Planning: Concurrent with the commencement of due diligence, full attention is required to determine the structure, resources, plans and teams for post-closing integration. Specific approaches and processes would be employed here to ensure that a proper integration leader is named (critical), robust but prioritized integration plans (e.g. IT and Finance integration might be a first priority for some companies), organizational and assimilation plans, and specific actions in several other area. Among the more difficult and critical elements of integration is culture. While culture is a key consideration in the pre-offer phases, it tends to be among the more challenging aspects to successful acquisitions and an area where experience from a career of hands-on accountability of acquisitions brings valuable insights. Several pro-active approaches can be introduced to the clients to determine which is best to employ with any particular integration.
Execution: From plans to execution requires much more than a roadmap. While such roadmaps are critical, it is the confluence of leadership and human capital, prioritized focused actions to achieve specific results, and finally sustainable integration to bring into the client’s company the full potential of the value creation possible. Tools exist and can be created to provide structure and management support to achieve this consistently.

Important And Strategic Elements Of A Growth By Acquisition Approach
This program has thus far concentrated on the role that acquisition strategies play in driving growth.
However, this assumes that the acquisitions are carried out properly on its own. Experience has shown that acquisitions may both produce and destroy value, with the execution of the transaction typically making the difference.
The following are crucial and strategic elements that support successful acquisitions:
• Considering strategic fit: Purchasing merely for the sake of purchasing is little more than management hubris. The target businesses should in some manner meet the needs of the buyer’s company strategy (i.e. product or service line, geographic reach, etc.).
• Addressing culture fit: Due to cultural mismatches between the two merging organizations, some of the largest mergers in history have failed. It is important to take into account a company’s culture because it directly affects how it creates value.
• Doing thorough due diligence: This guarantees that the buyer “looks beneath the hood” of the company they are buying and that the price they are looking to pay for the company reflects its intrinsic value.
• Integration: Even when the share purchase agreement’s ink dries, the deal is not finalized. The two businesses must now start an integration process to ensure that they grow into something greater than the sum of their individual parts.
Methodology

Acquisitive Growth
It’s challenging to make this kind of acquisition successful. Seven fundamental operating principles are used by profitable corporate and financial purchasers, according to research. Almost all phases of the acquisition process, from the selection of candidates through post-merger management, are impacted by these ideas.
• Insist on cutting-edge operating tactics.
• If you can’t identify the leader, don’t make the deal.
• Provide top executives with significant incentives.
• Connect pay to variations in cash flow.
• Accelerate the rate of change.
• Encourage lively interactions between the board, managers, and owners.
• Employ the top acquirers.

Insist On Cutting-Edge Operating Tactics
High-profile leveraged buyouts like those of Duracell International, Uniroyal, and RJR Nabisco have garnered a lot of attention since the early 1980s. Prices, clever financial arrangements, and bargaining strategies have received a lot of attention. However, the other 2,200+ buyouts that took place during that time period and the fundamental changes in operational procedures that led to profitable outcomes for many of those businesses have received little attention. Although many observers think that LBO enterprises find hidden treasures in the market, more often than not, they only concentrate on enhancing operations.
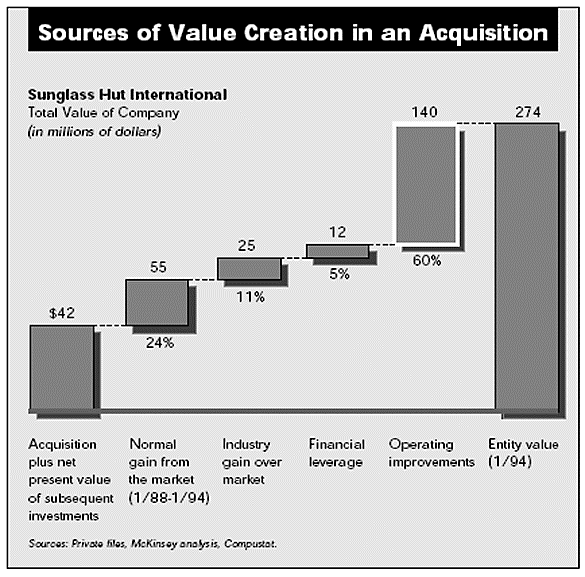
Two acquisitions, Sunglass Hut International and Snapple Beverage Corporation, show that operating performance—rather than financial leverage, market timing, or industry selection—is the main driver of value creation in successful acquisitions.
Desai Capital focused on accelerating sales growth and developed a new strategy to achieve so when it acquired Sunglass Hut. By acquiring smaller stores in turn and introducing a new store model, Sunglass Hut has expanded from 150 locations to more than 800 since the initial acquisition in 1988. This growth has led to an astounding 37% yearly return. The business introduced a broad product selection rather than depending on two or three popular lines, replaced clerks with limited knowledge of sunglasses with educated customer-service specialists, and implemented a low-cost regional approach.
Another illustration of operating improvements is the 1992 purchase of Snapple by renowned financial acquirer Thomas H. Lee Company. Snapple launched an aggressive growth strategy based on quick global expansion and product range extensions shortly after the takeover. The business immediately established its production and distribution network since it anticipated that rivals will soon release their own natural teas and fruit juices. It entered into contractual agreements with bottling and distribution businesses that had excess production capacity, allowing it to launch its product one year before major rivals like Fruitopia (from the Minute Maid division of Coca-Cola Company) and achieve a competitive advantage.
As the Snapple case demonstrates, innovative operating methods help acquirers succeed in fiercely competitive markets like the American food and beverage sector. The takeaway: Don’t limit your search for success to high-growing industries.


